Glossits is the catarrh of the tongue mucous membrane, which most often occurs as a manifestation of the stomatitis.
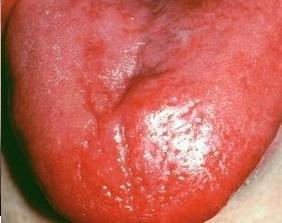
Glossitis is a disease, which causes pain in the tongue during meals and while making conversations; there is a painful reaction to any touch also during this problem. The tongue is changed in color, bloodshot, becomes edematous, dry and coated. The pain and discomfort increase with the expansion of erosion and ulcers. Symptoms and signs can vary in this case, depending on the causative factors.With superficial Glossitis, the tongue is bright red, painful, edematous, tight, and limited in movement. In the tongue, there is usually a burning sensation; the sense of taste is also lost. Patients suffer excessive salivation during this problem.
With deep glossitis, the inflammation is localized in the depth of the tongue as an abscess or cellulitis and often extends to the bottom of the mouth, which can cause the inflammation of the chin and the neck.According to dentists in Nebraska, the non-inflammatory glossitis forms include:

Benign migratory glossitis is also referred to as the ‘desquamative glossitis’, exfoliative glossitis or geographic tongue. It is marked by nidal destruction of the epithelium, red in color and surrounded by a crown on the back and lateral surfaces of the tongue. In 2-3 days, the epithelial layer is restored. Destruction and regeneration would be long and might be uneven: the nidi migrate and change the shape, which is why the tongue acquires the appearance of a map. In addition, there is sometimes a burning sensation in the tongue and pain while eating.
With median rhomboid glossitis, epithelium is thickened, and on the posterior tongue third in front of the valleculate papillae in the midline there is a clearly limited spot of rhomboid or oval form, usually bluish-red in color. This feature appears and disappears because median glossitis is a chronic disease. As a result of smoothing the affected papillae, the surface of the tongue looks varnished. In the future, papillomatosis excrescences covered in horny epithelium can appear. With palpation, certain induratin is noted, but there is no pain. The severity of the symptoms depends on the form of rhomboid glossitis. With flat glossitis, the surface of the nidus is smooth and looks polished; there are no tongue papillae there, whereas with verrucous form, lumpy dense growths are formed. In case of the papillomatoznye (hyperplastic) Glossitis, appearance of whitish-pink growths with a wide base and a flat top can be seen.
Atrophic glossitis (black hairy tongue) is marked by the growth and keratinization known as, filiform papillae, which are similar to the hairs varying in color from light yellow to black. They are formed mostly on the back of the tongue (the back third). The length of the filiform papillae sometimes reaches 1-2 cm. Patients are concerned about core throat and gagging. If you noticed the first symptoms of the disease, do not put off the visit to the dentist!
For any emergency occasion, you may also search for them here http://dentalprofy.com/dentists/oklahoma. Keep in mind, that timely detection of your condition will save your time and expenses for future treatment.








Comments are closed.